A modern JavaScript utility library delivering modularity, performance & extras.
lodash是一个一致性、模块化、高性能的JavaScript实用工具库
# 一、环境准备
lodash版本v4.0.0通过
github1s网页可以 查看 (opens new window)lodash - flatten源码调试测试用例可以
clone到本地
git clone https://github.com/lodash/lodash.git
cd axios
npm install
npm run test
# 二、结构分析
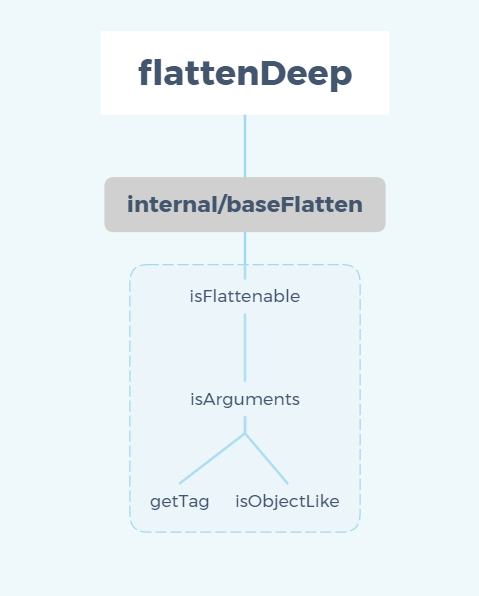
本篇主要讲述 flattenDeep 模块,包含 getTag、isObjectLike、isArguments、isFlattenable、baseFlatten。
# 三、函数研读
# 1. internal/getTag 模块
const toString = Object.prototype.toString;
/**
* Gets the `toStringTag` of `value`.
*
* @private
* @param {*} value The value to query.
* @returns {string} Returns the `toStringTag`.
*/
function getTag(value) {
if (value == null) {
return value === undefined ? "[object Undefined]" : "[object Null]";
}
return toString.call(value);
}
export default getTag;
- 使用非严格等
==无法判断value是nullorundefined - 使用严格等
===判断value是nullorundefined并设定 toStringTag (opens new window)(准确的说应该是Symbol.toStringTag) - 如果
nullorundefined直接使用Object原型链函数toString()获取toStringTag
Tips:许多内置的 JavaScript 对象类型即便没有 toStringTag 属性,也能被 toString() 方法识别并返回特定的类型标签,比如:Object.prototype.toString.call([1, 2]); // "[object Array]",但是有些对象类型则不然,toString() 方法能识别它们是因为引擎为它们设置好了 toStringTag 标签,比如:Object.prototype.toString.call(new Map()); // "[object Map]"
# 2. isObjectLike 模块
检查“value”是否与对象类似,如果不为空则是一个对象,并且会有一个“typeof”运算结果为“object”返回值
/**
* @since 4.0.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to check.
* @returns {boolean} Returns `true` if `value` is object-like, else `false`.
* @example
*
* isObjectLike({})
* // => true
*
* isObjectLike([1, 2, 3])
* // => true
*
* isObjectLike(Function)
* // => false
*
* isObjectLike(null)
* // => false
*/
function isObjectLike(value) {
return typeof value === 'object' && value !== null
}
export default isObjectLike
- 可以通过
typeof来获取未经计算的操作数的类型,下面是一个typeof运算结果集
| 类型 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| Undefined | "undefined" |
| Null | "object" |
| Boolean | "boolean" |
| Number | "number" |
| BigInt(ECMAScript 2020 新增) | "bigint" |
| String | "string" |
| Symbol (ECMAScript 2015 新增) | "symbol" |
| 宿主对象(由 JS 环境提供) | 取决于具体实现 |
| Function 对象 (按照 ECMA-262 规范实现 [[Call]]) | "function" |
| 其他任何对象 | "object" |
# 3. isArguments 模块
检查'value'是否与'arguments'对象类似
import getTag from './.internal/getTag.js'
import isObjectLike from './isObjectLike.js'
/**
* @since 0.1.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to check.
* @returns {boolean} Returns `true` if `value` is an `arguments` object, else `false`.
* @example
*
* isArguments(function() { return arguments }())
* // => true
*
* isArguments([1, 2, 3])
* // => false
*/
function isArguments(value) {
return isObjectLike(value) && getTag(value) == '[object Arguments]'
}
export default isArguments
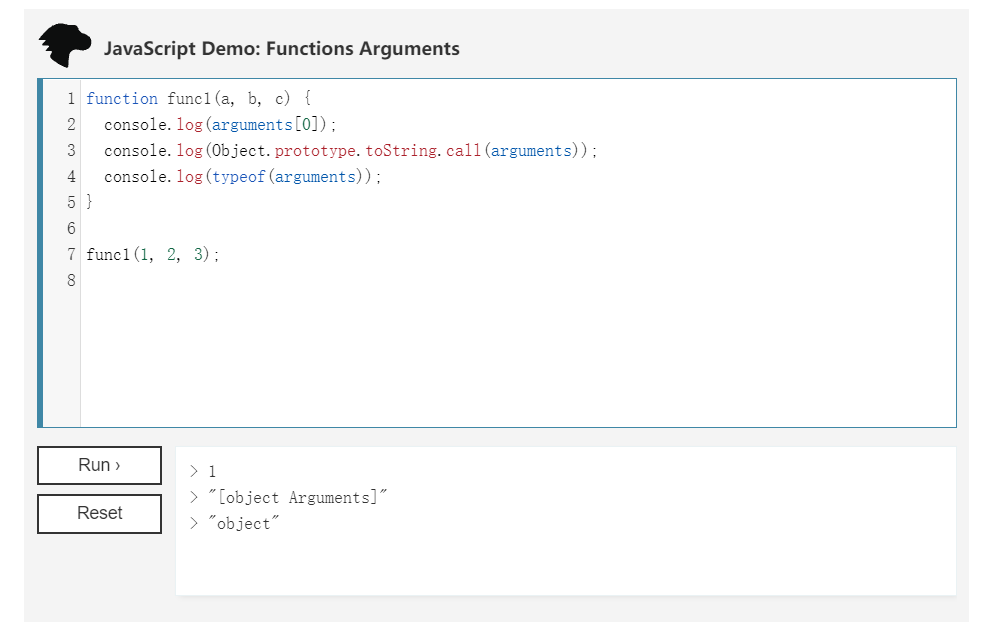
arguments对象是所有(非箭头)函数中都可用的局部变量。你可以使用arguments对象在函数中引用函数的参数。此对象包含传递给函数的每个参数,第一个参数在索引0处。- 需要注意的是,
arguments对象不是一个Array,它类似于Array,但除了length属性和索引元素之外没有任何Array属性。例如,它没有pop方法。 arguments对象只能在函数内使用,对其使用Object.prototype.toString.call(arguments)运算的返回值是[object Arguments]
# 4. isFlattenable 模块
检查'value'是否为可展平的'arguments'对象或数组
import isArguments from '../isArguments.js'
/** Built-in value reference. */
const spreadableSymbol = Symbol.isConcatSpreadable
/**
* @private
* @param {*} value The value to check.
* @returns {boolean} Returns `true` if `value` is flattenable, else `false`.
*/
function isFlattenable(value) {
return Array.isArray(value) || isArguments(value) ||
!!(value && value[spreadableSymbol])
}
export default isFlattenable
- 重点关注
value[spreadableSymbol],在这之前我们需要知道Array的concat运算,正常情况下['a', 'b', 'c'].concat([1, 2, 3]) = ["a", "b", "c", 1, 2, 3],但可通过设定被连接array,array[Symbol.isConcatSpreadable] = false;,使得array不被展开到发起连接的array而是作为一个元素连接到其中,如['a', 'b', 'c'].concat([1, 2, 3]) = ["a", "b", "c", [ 1, 2, 3] ] - 前文介绍过
!!运算符表示逻辑非的取反运算,如!!obj与obj != null && typeof obj === undefined && obj != "" && obj != false在计算上等价
# 5. baseFlatten 模块
扁平化”的基本实现,支持限制扁平化
import isFlattenable from './isFlattenable.js'
/**
* @private
* @param {Array} array The array to flatten.
* @param {number} depth 最大递归深度
* @param {boolean} [predicate=isFlattenable] 每次迭代调用的函数
* @param {boolean} [isStrict] 限制为通过“谓词”检查的值
* @param {Array} [result=[]] 初始结果值
* @returns {Array} 返回新的展平数组
*/
function baseFlatten(array, depth, predicate, isStrict, result) {
predicate || (predicate = isFlattenable)
result || (result = [])
if (array == null) {
return result
}
for (const value of array) {
if (depth > 0 && predicate(value)) {
if (depth > 1) {
// 递归展平阵列(易受调用堆栈限制的影响)
baseFlatten(value, depth - 1, predicate, isStrict, result)
} else {
result.push(...value)
}
} else if (!isStrict) {
result[result.length] = value
}
}
return result
}
export default baseFlatten
- 如果待展平数组
array是null,直接返回result(result=[]) - 使用
for...of迭代待展平array中的每一项,如果最大递归深度depth仍然未减至1则递归调用baseFlatten,每次depth - 1,直至depth = 1将返回值放入result。 depth = 1时由于所有项都已展平predicate(value)返回false,进入else if (!isStrict)语句块,目的是限制“谓词”展平到result,这里我们就需要了解谓词的概念了- 谓词是一个可调用的表达式,其返回结果是一个能用作条件的值。通俗的说就是一个函数,会返回一个符合该条件(“truthy值”)的数组🐶
# 6. flattenDeep 模块
将array递归为一维数组
import baseFlatten from './.internal/baseFlatten.js'
/** 无穷大,用作各种"Number"常量的引用 */
const INFINITY = 1 / 0
/**
* 递归展平`数组`
*
* @since 3.0.0
* @category Array
* @param {Array} array 需要处理的数组
* @returns {Array} 返回一个的新一维数组
* @see flatMap, flatMapDeep, flatMapDepth, flatten, flattenDepth
* @example
*
* flattenDeep([1, [2, [3, [4]], 5]])
* // => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
*/
function flattenDeep(array) {
const length = array == null ? 0 : array.length
return length ? baseFlatten(array, INFINITY) : []
}
export default flattenDeep
- 使用非严格等
==判断array是nullorundefined,如果是返回空数组,否则取array.length - 如果
array不是空数组,使用无穷大INFINITY递归调用baseFlatten(array, INFINITY)并返回
