A modern JavaScript utility library delivering modularity, performance & extras.
lodash是一个一致性、模块化、高性能的JavaScript实用工具库
# 一、环境准备
lodash版本v4.0.0通过
github1s网页可以 查看 (opens new window)lodash - drop源码调试测试用例可以
clone到本地
git clone https://github.com/lodash/lodash.git
cd axios
npm install
npm run test
# 二、结构分析
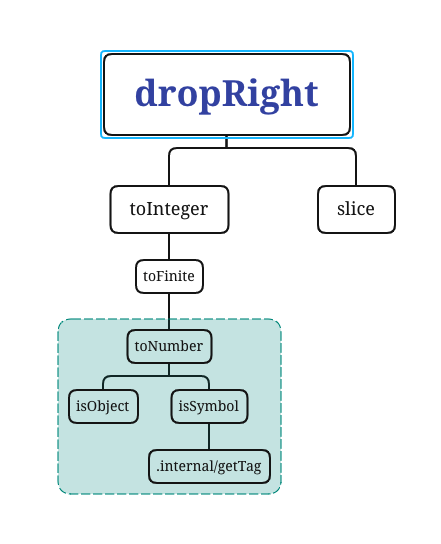
这是一张 dropRight 依赖引用路径图,其中使用到了 slice、toInteger、toFinite、toNumber、isObject、isSymbol、internal/getTag,接下来会自底向上分析各个依赖模块。
# 三、函数研读
# 1. internal/getTag 模块
获取 value 的 toStringTag
const toString = Object.prototype.toString;
/**
* @private
* @param {*} value The value to query.
* @returns {string} Returns the `toStringTag`.
*/
function getTag(value) {
if (value == null) {
return value === undefined ? "[object Undefined]" : "[object Null]";
}
return toString.call(value);
}
export default getTag;
- 使用非严格等
==无法判断value是nullorundefined - 使用严格等
===判断value是nullorundefined并设定 toStringTag (opens new window)(准确的说应该是Symbol.toStringTag) - 如果
nullorundefined直接使用Object原型链函数toString()获取toStringTag
Tips:许多内置的 JavaScript 对象类型即便没有 toStringTag 属性,也能被 toString() 方法识别并返回特定的类型标签,比如:Object.prototype.toString.call([1, 2]); // "[object Array]",但是有些对象类型则不然,toString() 方法能识别它们是因为引擎为它们设置好了 toStringTag 标签,比如:Object.prototype.toString.call(new Map()); // "[object Map]"
# 2. isSymbol 模块
检查 value 是否是原始 Symbol 或者对象
import getTag from "./.internal/getTag.js";
/**
* @since 4.0.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to check.
* @returns {boolean} Returns `true` if `value` is a symbol, else `false`.
* @example
*
* isSymbol(Symbol.iterator)
* // => true
*
* isSymbol('abc')
* // => false
*/
function isSymbol(value) {
const type = typeof value;
return (
type == "symbol" ||
(type === "object" &&
value != null &&
getTag(value) == "[object Symbol]")
);
}
export default isSymbol;
- 可以通过
typeof来获取未经计算的操作数的类型
# 3. isObject 模块
检查 value 是否为 Object 的language type (opens new window)。 (例如: arrays, functions, objects, regexes,new Number(0), 以及 new String(''))
/**
* @since 0.1.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to check.
* @returns {boolean} Returns `true` if `value` is an object, else `false`.
* @example
*
* isObject({})
* // => true
*
* isObject([1, 2, 3])
* // => true
*
* isObject(Function)
* // => true
*
* isObject(null)
* // => false
*/
function isObject(value) {
const type = typeof value;
return value != null && (type === "object" || type === "function");
}
export default isObject;
- 检查 value 是否是普通对象,即排除掉 null 类型的所有对象类型,包含 array、date、function 等对象类型
# 4. toNumber 模块
转换 value 为一个数字
import isObject from "./isObject.js";
import isSymbol from "./isSymbol.js";
/** 用作各种“数字”常量的引用 */
const NAN = 0 / 0;
/** 用于匹配前导和尾随空格 */
const reTrim = /^\s+|\s+$/g;
/** 用于检测错误的有符号十六进制字符串值 */
const reIsBadHex = /^[-+]0x[0-9a-f]+$/i;
/** 用于检测二进制字符串值 */
const reIsBinary = /^0b[01]+$/i;
/** 用于检测八进制字符串值 */
const reIsOctal = /^0o[0-7]+$/i;
/** 不依赖 `root` 的内置方法引用 */
const freeParseInt = parseInt;
/**
* @since 4.0.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to process.
* @returns {number} Returns the number.
* @see isInteger, toInteger, isNumber
* @example
*
* toNumber(3.2)
* // => 3.2
*
* toNumber(Number.MIN_VALUE)
* // => 5e-324
*
* toNumber(Infinity)
* // => Infinity
*
* toNumber('3.2')
* // => 3.2
*/
function toNumber(value) {
if (typeof value === "number") {
return value;
}
if (isSymbol(value)) {
return NAN;
}
if (isObject(value)) {
const other =
typeof value.valueOf === "function" ? value.valueOf() : value;
value = isObject(other) ? `${other}` : other;
}
if (typeof value !== "string") {
return value === 0 ? value : +value;
}
value = value.replace(reTrim, "");
const isBinary = reIsBinary.test(value);
return isBinary || reIsOctal.test(value)
? freeParseInt(value.slice(2), isBinary ? 2 : 8)
: reIsBadHex.test(value)
? NAN
: +value;
}
export default toNumber;
NAN是一个不可写、不可配置、不可枚举的数据类型,表示未定义或不可表示的值。常在浮点数运算中使用。首次引入 NaN 的是 1985 年的 IEEE 754 浮点数标准。比如 0/0、0×∞、∞ + (−∞)、∞ - ∞、NANx1、ix1 等计算结果均会返回NAN如果是 Number 类型则直接返回,如果是 symbol 类型返回
NANvalueOf() 方法返回指定对象的原始值,配合
typeof value.valueOf === "function",如果是function类型则会返回函数本身,如果是其他非null类型的 object 类型,则会返回对象本身如果是非 string 类型且不为 0 则使用 + 操作符转换成 Number 类型
去掉首尾空格
在返回前对二进制、八进制、十六进制数据格式做最后检查,如果正确就使用 + 操作符转换成 Number 类型返回否则返回 NUll 🐶
# 5. toFinite 模块
转换 value 为一个有限数字
import toNumber from "./toNumber.js";
/** 用作各种“数字”常量的引用 */
const INFINITY = 1 / 0;
const MAX_INTEGER = 1.7976931348623157e308;
/**
* @since 4.12.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to convert.
* @returns {number} Returns the converted number.
* @example
*
* toFinite(3.2)
* // => 3.2
*
* toFinite(Number.MIN_VALUE)
* // => 5e-324
*
* toFinite(Infinity)
* // => 1.7976931348623157e+308
*
* toFinite('3.2')
* // => 3.2
*/
function toFinite(value) {
if (!value) {
return value === 0 ? value : 0;
}
value = toNumber(value);
if (value === INFINITY || value === -INFINITY) {
const sign = value < 0 ? -1 : 1;
return sign * MAX_INTEGER;
}
return value === value ? value : 0;
}
export default toFinite;
- 首先拿到 toNumber 返回的 value 值,判断是否为正负无穷,然后根据其正负状态转换成 js 可以表示的双精度浮点数。其中使用常量
INFINITY = 1 / 0表示无穷。
# 6. toInteger 模块
转换 value 为一个整数
import toFinite from "./toFinite.js";
/**
* **Note:** This method is loosely based on
* [`ToInteger`](http://www.ecma-international.org/ecma-262/7.0/#sec-tointeger).
*
* @since 4.0.0
* @category Lang
* @param {*} value The value to convert.
* @returns {number} Returns the converted integer.
* @see isInteger, isNumber, toNumber
* @example
*
* toInteger(3.2)
* // => 3
*
* toInteger(Number.MIN_VALUE)
* // => 0
*
* toInteger(Infinity)
* // => 1.7976931348623157e+308
*
* toInteger('3.2')
* // => 3
*/
function toInteger(value) {
const result = toFinite(value);
const remainder = result % 1;
return remainder ? result - remainder : result;
}
export default toInteger;
- 将 value 转换成整形操作步骤很简单,关键在于处理各种边界情况,相信也是日常开发以及面试的考察点。
- 这里主要是使用了 toFinite 做了边界处理,然后使用求余运算
Number.MIN_VALUE的余数为其本身,其余整数余数为 0 的性质将Number.MIN_VALUE返回值置成 0
# 7. slice 模块
裁剪数组array,从 start 位置开始到end结束,但不包括 end 本身的位置
/**
* **Note:** This method is used instead of
* [`Array#slice`](https://mdn.io/Array/slice) to ensure dense arrays are
* returned.
*
* @since 3.0.0
* @category Array
* @param {Array} array The array to slice.
* @param {number} [start=0] The start position. 负索引将被视为与末尾的偏移量
* @param {number} [end=array.length] The end position. 负索引将被视为与末尾的偏移量
* @returns {Array} Returns the slice of `array`.
* @example
*
* var array = [1, 2, 3, 4]
*
* _.slice(array, 2)
* // => [3, 4]
*/
function slice(array, start, end) {
let length = array == null ? 0 : array.length;
if (!length) {
return [];
}
start = start == null ? 0 : start;
end = end === undefined ? length : end;
if (start < 0) {
start = -start > length ? 0 : length + start;
}
end = end > length ? length : end;
if (end < 0) {
end += length;
}
length = start > end ? 0 : (end - start) >>> 0;
start >>>= 0;
let index = -1;
const result = new Array(length);
while (++index < length) {
result[index] = array[index + start];
}
return result;
}
export default slice;
- 如果 array 是 null 直接返回空数组
- 如果 start 是 null 则默认为 0
- 如果 end 未定义则默认为 array 的 length 值
- start 为负数即负索引,则将被视为与末尾的偏移量,需要注意的是如果偏移量大于 length 则默认为 0
- end 为负数即负索引,则将被视为与末尾的偏移量,若为正数即正索引且大于 length 则默认与 length 值相等
- 根据 start 与 end 计算返回区间,其中
>>> 0确保了 start 和 length 落在 js 双精度有效表达范围【0 ~ 0xFFFFFFFF】中,详情可以查看js 中表达式 >>> 0 浅析 (opens new window) - 最后使用
new Array(length)重新创建一个 slice 数组并逐一赋值后返回
# 8. dropRight 模块
创建一个array片段,从末尾删除n个元素
import slice from './slice.js'
import toInteger from './toInteger.js'
/**
* @since 3.0.0
* @category Array
* @param {Array} array The array to query.
* @param {number} [n=1] The number of elements to drop.
* @returns {Array} Returns the slice of `array`.
* @example
*
* dropRight([1, 2, 3])
* // => [1, 2]
*
* dropRight([1, 2, 3], 2)
* // => [1]
*
* dropRight([1, 2, 3], 5)
* // => []
*
* dropRight([1, 2, 3], 0)
* // => [1, 2, 3]
*/
function dropRight(array, n=1) {
const length = array == null ? 0 : array.length
n = length - toInteger(n)
return length ? slice(array, 0, n < 0 ? 0 : n) : []
}
export default dropRight
array为null或undefined,则length = 0否则取array.lengtharray为null或undefined或[]返回[],否则进入slice逻辑
# 四、参考
1. 探秘 JavaScript 世界的神秘數字 1.7976931348623157e+308 (opens new window)
